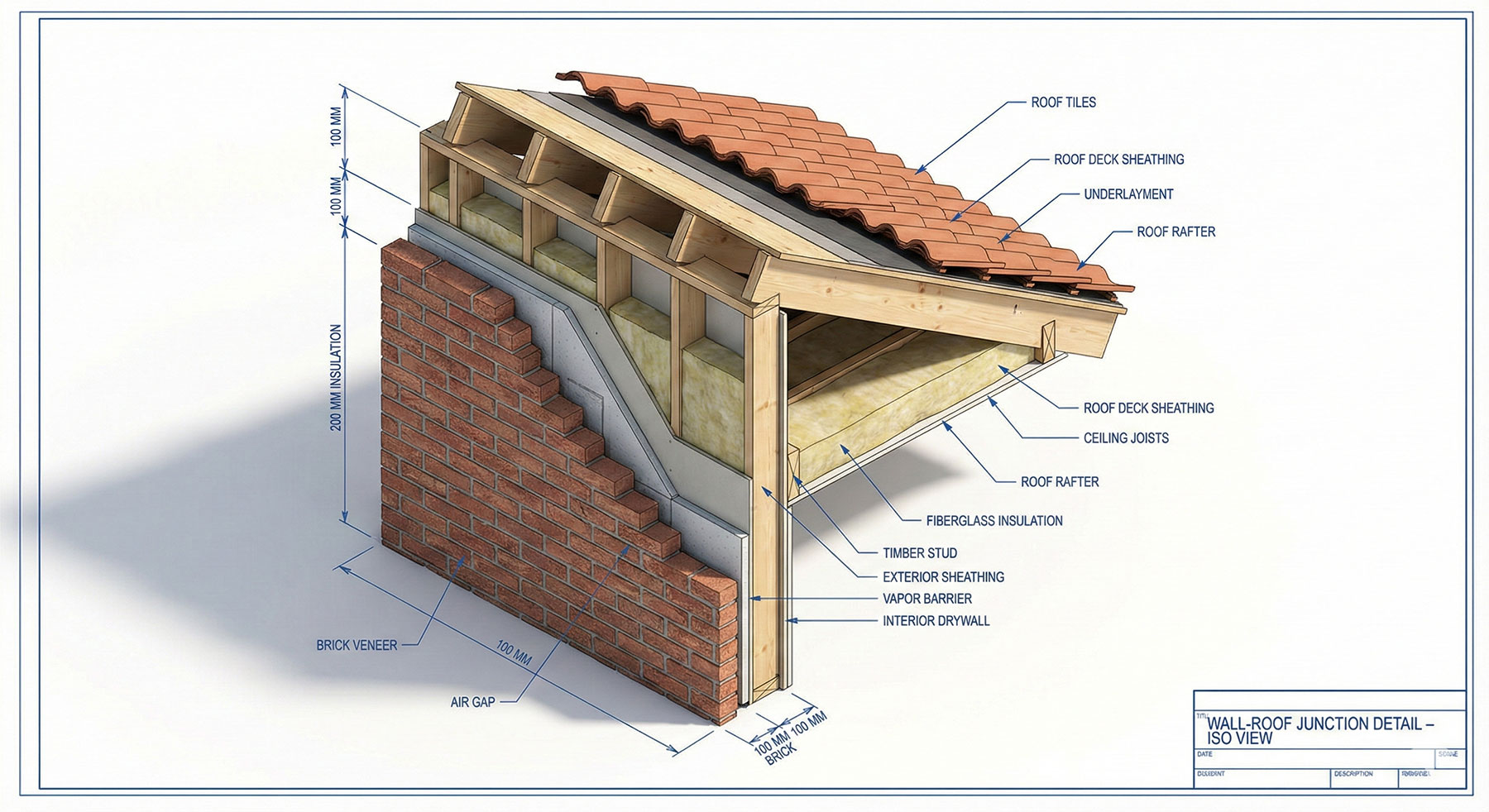
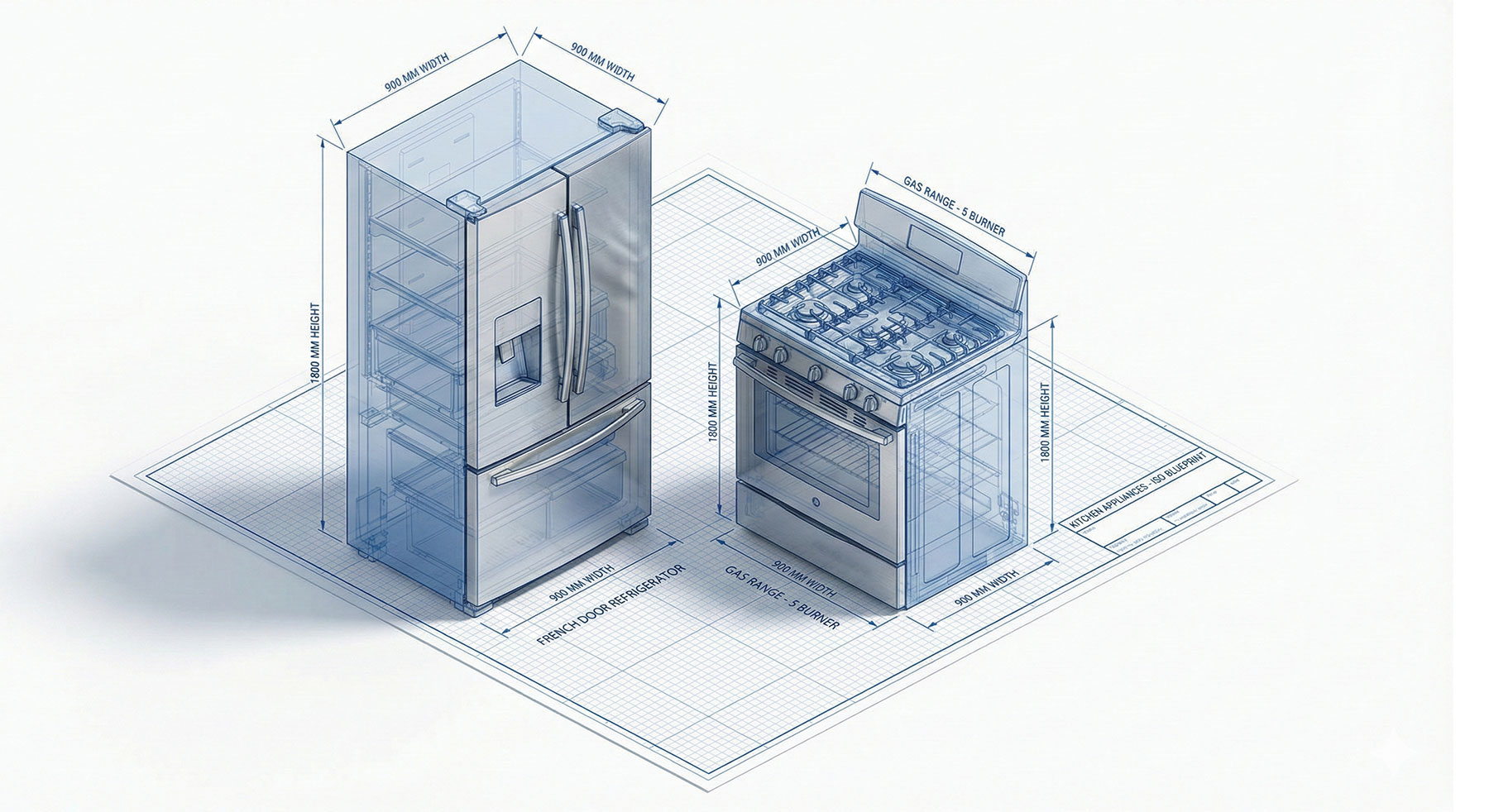
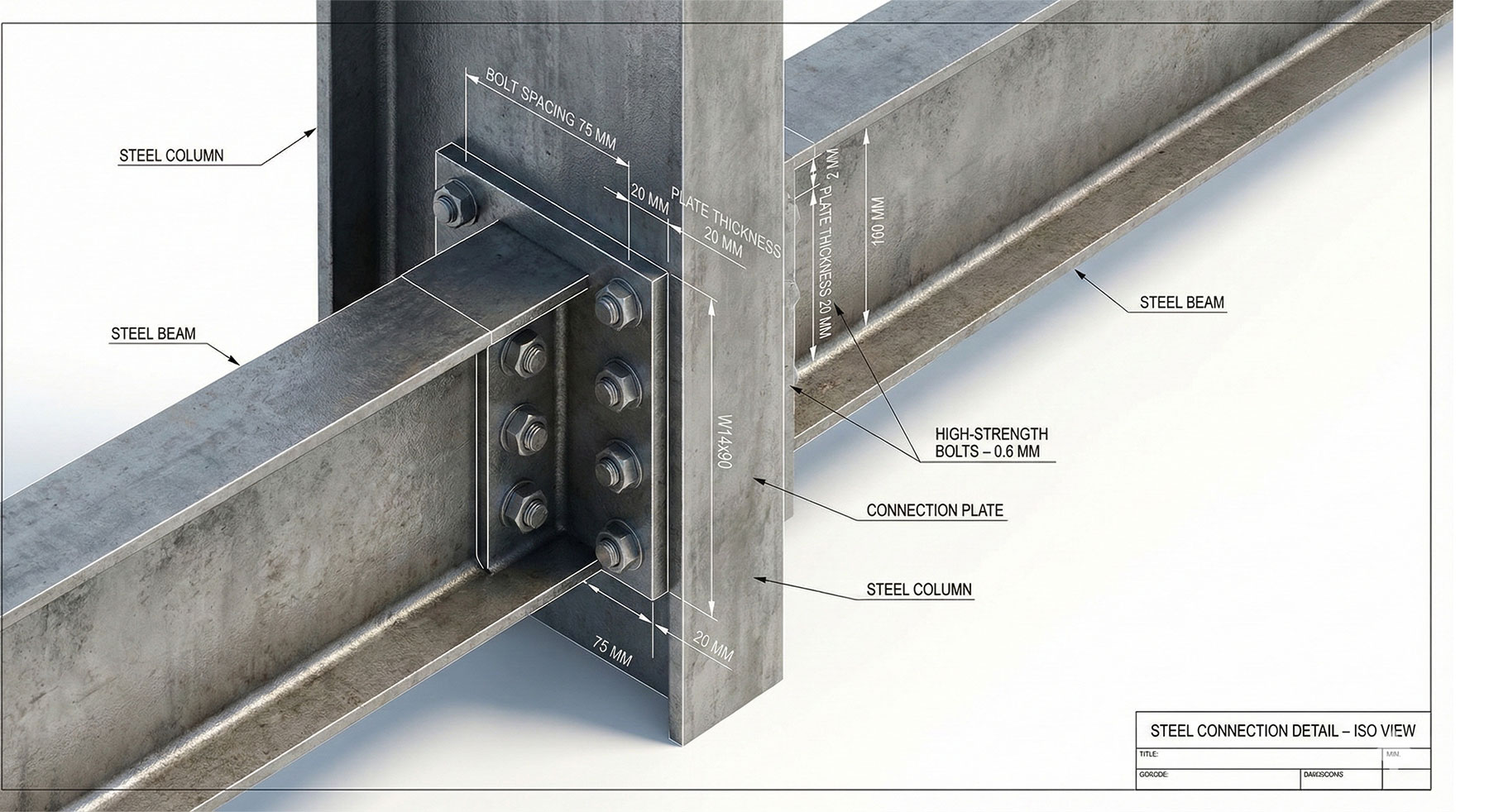
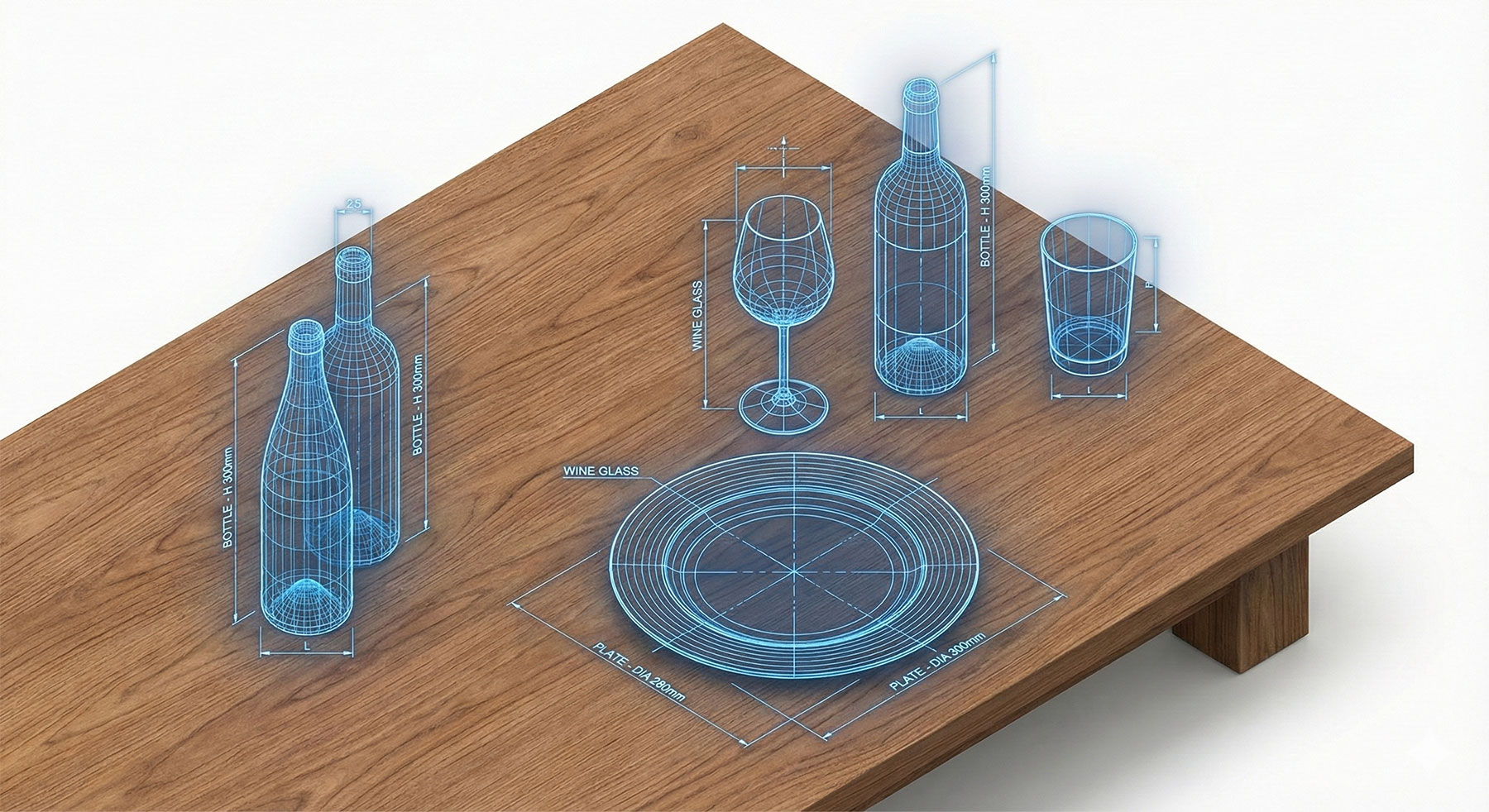
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Guide for Architects
01/04/2025The Ultimate Guide to Interior Design in BIM topics
What is BIM?
The Role of BIM in Interior Design
Benefits of Interior Design in BIM
BIM Levels and Interior Design
BIM Software for Interior Design
BIM Objects and Interior Design
Collaboration and Communication in Interior Design with BIM
Challenges and Solutions in Interior Design with BIM
Case Studies:
Successful Implementation of BIM in Interior Design
The Future of Interior Design in BIM
1. What is BIM?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a holistic process that involves creating and managing information for a built asset. It is based on an intelligent model and enabled by a cloud platform. BIM integrates structured, multi-disciplinary data to produce a digital representation of an asset across its lifecycle, from planning and design to construction and operations[^1^].
2. The Role of BIM in Interior Design
Interior design plays a crucial role in creating functional, aesthetically pleasing, and sustainable spaces within buildings. Traditionally, interior design relied on 2D drawings and manual coordination, which often led to errors, clashes, and inefficiencies. With the advent of BIM, interior design has been transformed into a streamlined and collaborative process.
BIM allows interior designers to work in a 3D virtual environment, creating accurate and detailed models of interior spaces. These models can include furniture, fixtures, finishes, and other elements, providing a realistic representation of the final design. BIM also enables designers to visualize how different materials, colors, and lighting will interact in the space, enhancing the decision-making process[^2^].
3. Benefits of Interior Design in BIM
Implementing interior design in BIM offers numerous benefits for all stakeholders involved in the project. Some of the key benefits include:
a. Improved Collaboration and Coordination
BIM facilitates seamless collaboration and coordination among architects, engineers, contractors, and interior designers. With a shared 3D model, all professionals can work together in real-time, reducing clashes, errors, and rework. This collaborative approach ensures that the interior design aligns with the overall building design, resulting in a harmonious and integrated space.
b. Enhanced Visualization and Communication
BIM allows interior designers to visualize their concepts in a realistic 3D environment. They can create virtual walkthroughs, flyovers, and renderings to showcase their design intent to clients and other stakeholders. This enhances communication and ensures that everyone involved has a clear understanding of the design vision.
c. Efficient Space Planning and Layout
Interior designers can use BIM to optimize space planning and layout. They can easily test different configurations, furniture arrangements, and circulation patterns to maximize space utilization and functionality. BIM also enables designers to analyze daylighting, acoustics, and thermal performance, ensuring a comfortable and sustainable interior environment.
d. Streamlined Material Selection and Specification
BIM allows interior designers to access a vast library of BIM objects, which are intelligent components with geometry and data. These objects can be easily integrated into the model, eliminating the need for manual drafting and specification. Interior designers can select and visualize different materials, finishes, and furnishings, making informed decisions based on accurate data.
e. Cost and Time Savings
By working in a collaborative BIM environment, interior designers can identify clashes and conflicts early in the design phase, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming changes during construction. BIM also enables better cost estimation and budget tracking, helping to optimize the use of resources and minimize waste.
4. BIM Levels and Interior Design
BIM is often categorized into different levels, which represent the maturity and extent of BIM implementation in a project. Each level has specific criteria and requirements. Let’s explore how these levels relate to interior design:
a. Level 0 BIM: Paper-based Drawings and Limited Collaboration
At Level 0, interior design is typically based on 2D drawings and lacks collaborative coordination. Designers may use CAD software for drafting, but the exchange of information is limited, and there is minimal integration between disciplines.
b. Level 1 BIM: 2D Drawings and Basic 3D Modeling
Level 1 introduces basic 3D modeling capabilities, allowing interior designers to create simple 3D representations of their designs. However, collaboration and coordination are still limited, and each discipline manages its own data without a centralized environment.
c. Level 2 BIM: Collaborative 3D Modeling
Level 2 BIM is characterized by a collaborative working environment, where all stakeholders use 3D models for their respective disciplines. Interior designers can work on their 3D models, which are then federated into a shared model. This level of BIM requires the use of open file formats, such as IFC (Industry Foundation Class), for data exchange.
d. Level 3 BIM: Shared Project Model
At Level 3, interior designers work on a shared project model, where all stakeholders can access and modify the model simultaneously. This level of BIM enables real-time collaboration and coordination, enhancing communication and reducing clashes. Advanced technologies, such as cloud-based platforms and collaboration tools, are essential for Level 3 implementation.
e. Beyond Level 3: Adding Time, Cost, and Sustainability Information
Levels 4, 5, and 6 BIM involve the integration of additional information into the model, such as scheduling, cost estimation, and sustainability data. While these levels are not exclusive to interior design, they offer further opportunities for optimizing the interior design process and improving the overall performance of the built environment.
5. BIM Software for Interior Design
To effectively implement interior design in BIM, specialized software tools are essential. These tools offer a range of features and functionalities specifically designed for interior designers. Here are some popular BIM software options for interior design:
a. Autodesk Revit
Revit is a comprehensive BIM software that provides a range of tools for architects, engineers, and interior designers. It allows designers to create detailed 3D models, generate construction documentation, and collaborate with other professionals. Revit offers a wide range of built-in objects and materials specifically tailored for interior design.
b. ARCHICAD
ARCHICAD is another powerful BIM software that offers advanced modeling capabilities for interior design. It enables designers to create detailed 3D models, generate accurate construction drawings, and perform energy analysis. ARCHICAD also supports Open BIM workflows, allowing seamless collaboration with professionals using different software tools.
c. Vectorworks Architect
Vectorworks Architect is a versatile BIM software that offers comprehensive tools for interior design. It allows designers to create detailed 3D models, generate construction documentation, and perform visualizations. Vectorworks also offers a wide range of plugins and libraries specifically tailored for interior design.
d. SketchUp
While not a full-fledged BIM software, SketchUp is widely used in the industry for conceptual modeling and interior design. It offers a user-friendly interface and powerful 3D modeling capabilities. SketchUp allows designers to quickly create and visualize interior spaces, making it an ideal tool for early-stage design exploration.
6. BIM Objects and Interior Design
BIM objects play a crucial role in interior design within the BIM environment. These objects are intelligent components that have both geometry and data. They represent real-world products, such as furniture, fixtures, finishes, and equipment. By using BIM objects, interior designers can easily incorporate manufacturer-specific products into their models, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
BIM objects are typically available in online libraries, where designers can search and download objects for their projects. These objects come with predefined properties and parameters, such as dimensions, materials, and performance data. Interior designers can customize these objects to suit their specific design requirements, saving time and effort in the modeling process.
7. Collaboration and Communication in Interior Design with BIM
One of the key advantages of BIM in interior design is its ability to facilitate collaboration and communication among project stakeholders. Effective collaboration is essential for a successful interior design process, as it involves multiple professionals working together to achieve a common goal. BIM provides several tools and workflows to enhance collaboration and streamline communication.
a. Clash Detection and Coordination
BIM enables clash detection and coordination among different disciplines, including architecture, structure, MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing), and interior design. Clash detection tools automatically identify conflicts and clashes between different elements, such as walls, ceilings, and MEP systems. Interior designers can resolve these clashes in the virtual environment, reducing errors and rework during construction.
b. Model-Based Annotation and Markups
BIM allows interior designers to annotate and markup the 3D model, adding comments, dimensions, and other information directly onto the model. These annotations serve as a communication tool between designers, clients, and other stakeholders. Model-based annotations facilitate clear and concise communication, ensuring that design intent is accurately conveyed.
c. Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms
Cloud-based collaboration platforms, such as BIM 360 and Trimble Connect, enable real-time collaboration and data sharing among project stakeholders. These platforms provide a centralized environment where designers, contractors, and clients can access the latest project information, including 3D models, drawings, and documents. Cloud collaboration platforms enhance communication and streamline workflows, eliminating the need for manual file sharing and version control.
d. Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies are increasingly being used in interior design with BIM. These technologies allow designers and clients to immerse themselves in the virtual environment, experiencing the space before it is built. VR and AR enhance visualization and communication, helping to identify design issues and make informed decisions.
8. Challenges and Solutions in Interior Design with BIM
While BIM offers significant advantages for interior design, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. Some of the key challenges include:
a. Adoption and Training
The successful implementation of BIM in interior design requires proper adoption and training. Design professionals need to be familiar with BIM concepts, workflows, and software tools. Training programs and resources should be provided to ensure that designers have the necessary skills to effectively use BIM in their work.
b. Standardization and Interoperability
Standardization and interoperability are essential for seamless collaboration in the BIM environment. Designers, manufacturers, and software developers should adhere to open standards, such as IFC and COBie, to ensure the exchange of data between different platforms. Standardized object libraries and classification systems also enhance interoperability and consistency.
c. Data Management and Integration
Managing and integrating data from various sources is a challenge in interior design with BIM. Designers need to ensure that the data they use is accurate, up-to-date, and compatible with the BIM model. Data management systems and protocols should be established to maintain data integrity and facilitate efficient workflows.
d. Legal and Contractual Considerations
The legal and contractual aspects of interior design with BIM need to be carefully considered. Design professionals should define their roles, responsibilities, and liabilities in BIM contracts. Intellectual property rights, data ownership, and liability for errors and omissions should be clearly addressed to avoid potential disputes.
9. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of BIM in Interior Design
Several real-world projects have successfully implemented BIM in interior design. These case studies highlight the benefits and outcomes of using BIM in the design process. Let’s explore a few examples:
a. Project X: Office Space Renovation
In this project, BIM was used to renovate an existing office space. The interior design team created a detailed 3D model of the space, including furniture, finishes, and lighting. BIM enabled precise coordination with the architectural and MEP disciplines, resulting in a seamless and efficient renovation process. Clash detection tools helped identify potential conflicts, and virtual walkthroughs allowed stakeholders to visualize the final design.
b. Project Y: Hotel Interior Design
In the design of a new hotel, BIM was used to create a comprehensive interior design model. The model included guest rooms, common areas, and back-of-house spaces. BIM facilitated collaboration between the interior design team, the architect, and the contractor. By using BIM objects, the designers easily selected and specified furniture, fixtures, and finishes, ensuring accurate representation and efficient procurement.
c. Project Z: Retail Store Design
BIM was utilized in the design of a retail store, focusing on creating an immersive and engaging customer experience. BIM allowed the interior design team to experiment with different layouts, lighting scenarios, and material combinations. The 3D model was shared with the client, enabling them to provide feedback and make informed decisions. The project was completed on time and within budget, thanks to the efficient coordination facilitated by BIM.
10. The Future of Interior Design in BIM
The future of interior design in BIM is promising, with continued advancements in technology and workflows. Here are some trends and developments to watch out for:
a. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies have the potential to transform interior design in BIM. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to generate design options, optimize space utilization, and provide real-time performance feedback. ML algorithms can learn from past projects and recommend design solutions based on historical data.
b. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The integration of IoT devices with BIM models opens up new possibilities for interior design. Sensors embedded in buildings can provide real-time data on occupancy, temperature, and energy consumption, allowing designers to create more responsive and sustainable spaces. IoT integration enables designers to simulate and analyze the impact of different design choices on occupant comfort and building performance.
c. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR technologies will continue to play a significant role in interior design with BIM. Designers and clients can immerse themselves in virtual environments, experiencing the space before it is built. VR and AR enhance visualization, facilitate design reviews, and support decision-making. As VR and AR technologies become more accessible and affordable, their adoption in interior design will increase.
d. Parametric Design and Generative Algorithms
Parametric design and generative algorithms enable designers to explore a wide range of design options and find optimal solutions. By defining parameters and constraints, designers can generate multiple iterations of a design and evaluate their performance. Parametric design and generative algorithms facilitate data-driven design decisions and foster creativity in the interior design process.
As we look to the future, the integration of interior design with BIM will continue to evolve, offering exciting opportunities for innovation, sustainability, and collaboration. By embracing the power of BIM, interior designers can create extraordinary spaces that enhance the human experience.
In conclusion, interior design in BIM brings numerous benefits, including improved collaboration, enhanced visualization, efficient space planning, streamlined material selection, and cost savings.
The Ultimate Guide to Interior Design in BIM by leveraging specialized BIM software, utilizing BIM objects, and embracing collaborative workflows, interior designers can unlock the full potential of BIM. Despite challenges, the future of interior design in BIM holds immense potential, driven by advancements in AI, IoT, VR, and parametric design. It’s time for interior designers to embrace BIM and shape the future of the built environment.